Question 1. What is JNDI ?
Answer : It stands for Java Naming and Directory Interface. The Java Naming and Directory InterfaceTM (JNDI) is an application programming interface (API) that provides naming and directory functionality to applications written using the JavaTMprogramming language. It is defined to be independent of any specific directory service implementation. Thus a variety of directories(new, emerging, and already deployed) can be accessed in a common way.

To use the JNDI, you must have the JNDI classes and one or more service providers. The Java 2 SDK, v1.3 includes three service providers for the following naming/directory services:
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) Common Object Services (COS) name service
Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Registry
So basically you create objects and register them on the directory services which you can later do lookup and execute operation on.
JNDI allows distributed applications to look up services in an abstract, resource-independent way.
The most common use case is to set up a database connection pool on a Java EE application server. Any application that's deployed on that server can gain access to the connections they need using the JNDI name java:comp/env/FooBarPool without having to know the details about the connection.
This has several advantages:
If you have a deployment sequence where apps move from devl->int->test->prodenvironments, you can use the same JNDI name in each environment and hide the actual database being used. Applications don't have to change as they migrate between environments.
You can minimize the number of folks who need to know the credentials for accessing a production database. Only the Java EE app server needs to know if you use JNDI.
Question 2 : How to test the connection pool from console?
Answer : In order to see a Server/State and Test Data Source action listed under Services -> Data Sources -> -> Monitoring (Tab) -> Testing (Tab), all of the following need to be true:
At least one server targeted by the Data Source needs to be running. If the AdminServer is not targeted, this might not be true - visit Environment -> Servers and check that the targeted server(s) are RUNNING.
The Data Source's Configuration -> Connection Pool -> (Advanced) "Test Connections On Reserve" must be checked/true
You need to have a table-name configured in Test Table Name or an SQL statement e.g. SQL SELECT 1 FROM DUAL.
You should then see the targeted servers listed in the Monitoring/Testing tab.
Note: To make the test more meaningful, make sure that Test Reserved Connections or Test Released Connections is selected on the Configuration—>Connections tab (under Advanced Options). If either of these options is selected, WebLogic Server not only reserves and releases a connection, but also tests the physical database connection. See Test Reserved Connections in Attributes.
Question 3 : How to confirm that database server is accessible from WLS server?
Answer : Use the following Steps to make sure that you are able to connect to the DataBase Box from the WLS Server Box…
Step1). Add JDBC Driver also in the Classpath or Better run “setWLSEnv.sh”
Step2). Use WLS DB Ping utility:
Syntax:
java -classpath /bea103/wl_server103/server/lib/weblogic.jar utils.dbping ORACLE_THIN
Example:
java -classpath /bea103/wl_server103/server/lib/weblogic.jar utils.dbping ORACLE_THIN scott tiger databaseHostName:1521:myDB
Question 4 : What is the differences b/w unicast and multi cast?
Answer : WebLogic Server supports two cluster messaging protocols:
Multicast: This protocol relies on UDP multicast and has been supported in WebLogic Server clusters since WebLogic Server 4.0.
Unicast: This protocol relies on point-to-point TCP/IP sockets and was added in WebLogic Server 10.0.
The main difference between Unicast and Multicast is as follows
Say you have three servers (MS-1,MS-2,MS-3) in a cluster now if they have to communicate with each other they have to ping (i.e. heartbeats ) the cluster master for informing him that he is alive.
If MS-1 is the master then MS-2 and MS-3 would send the ping to MS-1
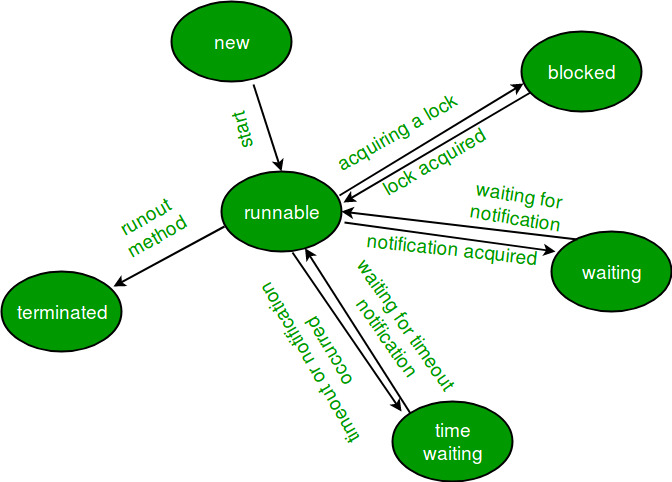
WAITING
A thread that is waiting indefinitely for another thread to perform a particular action is in this state.
TIMED_WAITING
A thread that is waiting for another thread to perform an action for up to a specified waiting time is in this state.
Answer : It stands for Java Naming and Directory Interface. The Java Naming and Directory InterfaceTM (JNDI) is an application programming interface (API) that provides naming and directory functionality to applications written using the JavaTMprogramming language. It is defined to be independent of any specific directory service implementation. Thus a variety of directories(new, emerging, and already deployed) can be accessed in a common way.

To use the JNDI, you must have the JNDI classes and one or more service providers. The Java 2 SDK, v1.3 includes three service providers for the following naming/directory services:
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) Common Object Services (COS) name service
Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) Registry
So basically you create objects and register them on the directory services which you can later do lookup and execute operation on.
JNDI allows distributed applications to look up services in an abstract, resource-independent way.
The most common use case is to set up a database connection pool on a Java EE application server. Any application that's deployed on that server can gain access to the connections they need using the JNDI name java:comp/env/FooBarPool without having to know the details about the connection.
This has several advantages:
If you have a deployment sequence where apps move from devl->int->test->prodenvironments, you can use the same JNDI name in each environment and hide the actual database being used. Applications don't have to change as they migrate between environments.
You can minimize the number of folks who need to know the credentials for accessing a production database. Only the Java EE app server needs to know if you use JNDI.
Question 2 : How to test the connection pool from console?
Answer : In order to see a Server/State and Test Data Source action listed under Services -> Data Sources -> -> Monitoring (Tab) -> Testing (Tab), all of the following need to be true:
At least one server targeted by the Data Source needs to be running. If the AdminServer is not targeted, this might not be true - visit Environment -> Servers and check that the targeted server(s) are RUNNING.
The Data Source's Configuration -> Connection Pool -> (Advanced) "Test Connections On Reserve" must be checked/true
You need to have a table-name configured in Test Table Name or an SQL statement e.g. SQL SELECT 1 FROM DUAL.
You should then see the targeted servers listed in the Monitoring/Testing tab.
Note: To make the test more meaningful, make sure that Test Reserved Connections or Test Released Connections is selected on the Configuration—>Connections tab (under Advanced Options). If either of these options is selected, WebLogic Server not only reserves and releases a connection, but also tests the physical database connection. See Test Reserved Connections in Attributes.
Question 3 : How to confirm that database server is accessible from WLS server?
Answer : Use the following Steps to make sure that you are able to connect to the DataBase Box from the WLS Server Box…
Step1). Add JDBC Driver also in the Classpath or Better run “setWLSEnv.sh”
Step2). Use WLS DB Ping utility:
Syntax:
java -classpath /bea103/wl_server103/server/lib/weblogic.jar utils.dbping ORACLE_THIN
Example:
java -classpath /bea103/wl_server103/server/lib/weblogic.jar utils.dbping ORACLE_THIN scott tiger databaseHostName:1521:myDB
Question 4 : What is the differences b/w unicast and multi cast?
Answer : WebLogic Server supports two cluster messaging protocols:
Multicast: This protocol relies on UDP multicast and has been supported in WebLogic Server clusters since WebLogic Server 4.0.
Unicast: This protocol relies on point-to-point TCP/IP sockets and was added in WebLogic Server 10.0.
The main difference between Unicast and Multicast is as follows
Unicast:
Say you have three servers (MS-1,MS-2,MS-3) in a cluster now if they have to communicate with each other they have to ping (i.e. heartbeats ) the cluster master for informing him that he is alive.
If MS-1 is the master then MS-2 and MS-3 would send the ping to MS-1
Multicast:
Here there is no cluster master each server has to ping each other to inform everyone that I am alive.
So MS-1 would send the ping to MS-2 & MS-3 same way MS-2 would send the ping to MS-1 & MS-3 and MS-3 would ping MS-1 & MS-3.
Thus if you see in multicast the congestion in sending the pings are more compared to unicast which makes multicast much heavier, thus WLS recommends using Unicast of less congestion in the network.
Question 5 :What are the different thread states in Java?
Answer :
Here there is no cluster master each server has to ping each other to inform everyone that I am alive.
So MS-1 would send the ping to MS-2 & MS-3 same way MS-2 would send the ping to MS-1 & MS-3 and MS-3 would ping MS-1 & MS-3.
Thus if you see in multicast the congestion in sending the pings are more compared to unicast which makes multicast much heavier, thus WLS recommends using Unicast of less congestion in the network.
Question 5 :What are the different thread states in Java?
Answer :
A thread state. A thread can be in one of the following states:
WAITING
A thread that is waiting indefinitely for another thread to perform a particular action is in this state.
TIMED_WAITING
A thread that is waiting for another thread to perform an action for up to a specified waiting time is in this state.
No comments:
Post a Comment